Here are some tools and definitions to make using WebSyn easier!
WebSyn is currently not designed for mobile users. Full functionality will only work on desktop (on any modern browser).
Very old computers might have trouble using it.
The main functionality is audio output, so a way to listen to audio is essential.
It is also made for a standard English language keyboard, so alternative layouts might have trouble
with the functionality
(for example, the Spanish language keyboard has a ñ instead of a ;, and the German keyboard has the Z and Y keys swapped
relative to the QWERTY layout).
Here is some info on
changing your computer's keyboard language if you need to.
Defines how loud the synthesizer is.
Defines how long it takes for the note to go from 0 to full volume in seconds.
Defines how long it takes for the note to go from full volume to sustain level in seconds, while the note is being held.
Defines the sustain level as a percentage of the full volume, which is held until the note is released.
Defines how long it takes for the level of the note to go from the sustain volume to 0 after the note is released (so, once you are not playing it anymore).
Octave
These buttons raise (+) and lower (-) the octave of the notes being played. You can also control them with the Z and X notes on your computer keyboard.
wave 1: wave 2:
WebSyn plays 2 oscillators at once. These menus let you choose from a series of different wave shapes what kind of wave you're hearing. The available wave shapes are:
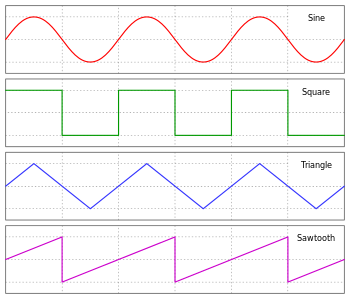
Source: Omegatron, CC BY-SA 3.0, link, via Wikimedia Commons
The slider balances how much of each you're hearing. 0 means you're only hearing the left waveshape, 1 only the right.
Playing the keyboard:
You can play the keyboard by clicking on the key buttons on the screen, as well as using your computer keyboard:
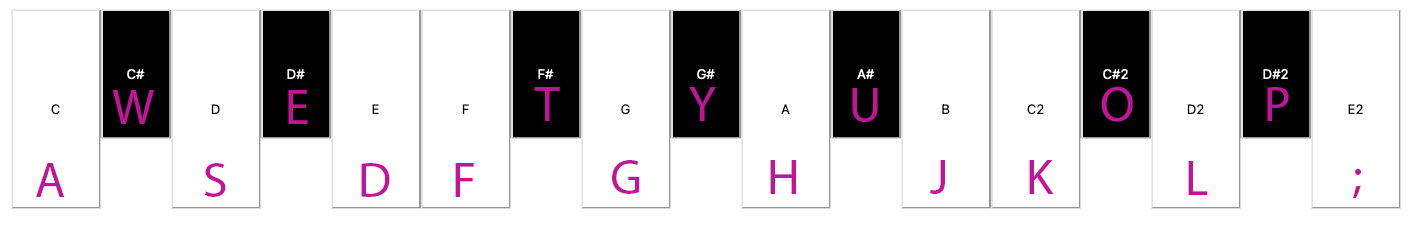
This lets you not only play more comfortably, but also several notes at once!
Comment: a known bug (which you can feel free to exploit) is if the same key is pressed several times in quick succession there is a high chance a note will start and never stop, creating an "infinite note".
Unfortunately, the only way to stop this is to reload the page.
Effects
filters
| low-pass | bell | high-pass |
|
A high-pass filter only "lets through" frequencies above its cutoff frequency and attenuates those below it. Use the "frequency" slider to adjust the cutoff frequency. 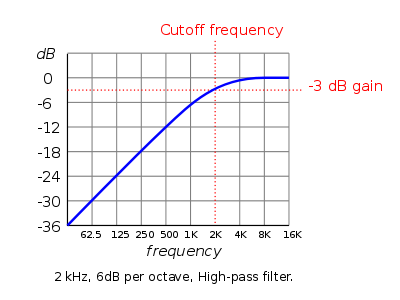
Source: Audacity Manual |
A bell or peaking filter selects a frequency (adjusted with the "frequency" slider) and turns it up or down by a value defined by the "gain" slider. The "Q" slider defines how many frequencies around the central one will be affected (a higher Q means fewer frequencies). 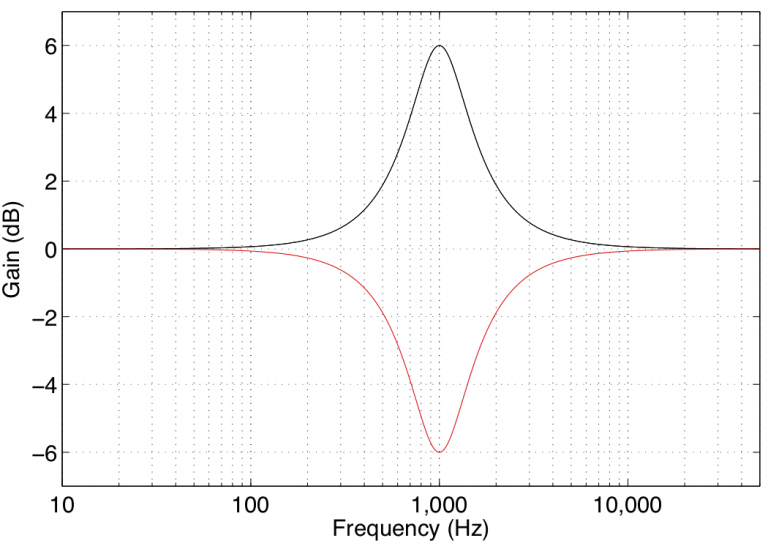
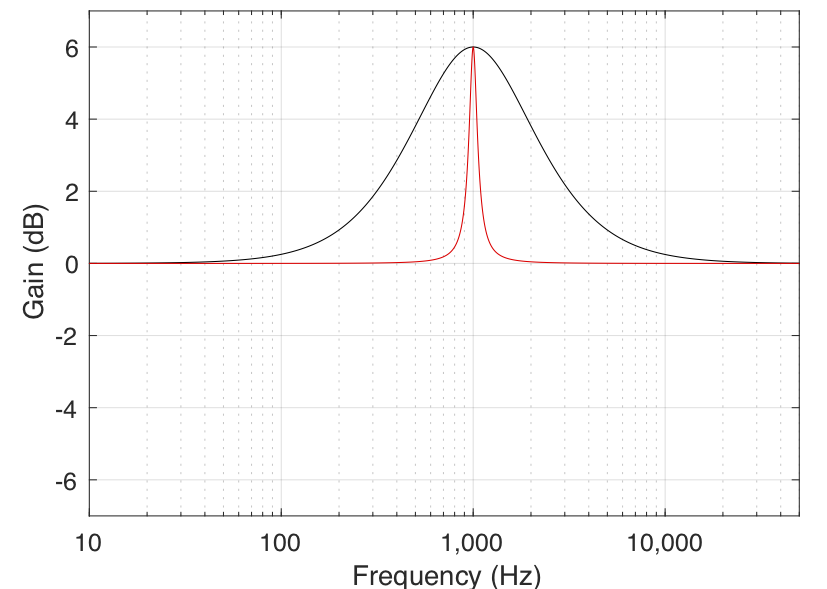
Source: Earfluff and Eyecandy |
A low-pass filter only "lets through" frequencies below its cutoff frequency and attenuates those above it. Use the "frequency" slider to adjust the cutoff frequency. 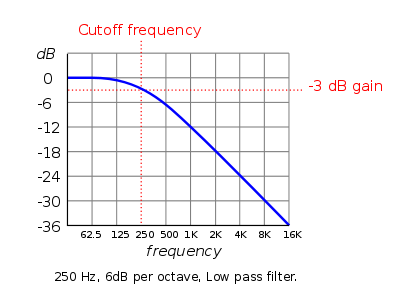
Source: Audacity Manual |
Distortion
Adds distortion!
Delay
A delay! "Time" defines how many seconds between repeats, "feedback" what proportion of the repeated audio gets delayed again, and "mix" how loud it is compared to the full volume of the dry signal.
Record
To record audio, press "start" and play whatever melody you want! To stop, press "stop". You can now listen to what you recorded and download it by right (or control-)clicking and choosing "Save Audio As..." or similar depending on your OS.
Tip: you can change parameters of the sound while recording!